How to Calculate Accounts Receivable Turnover?
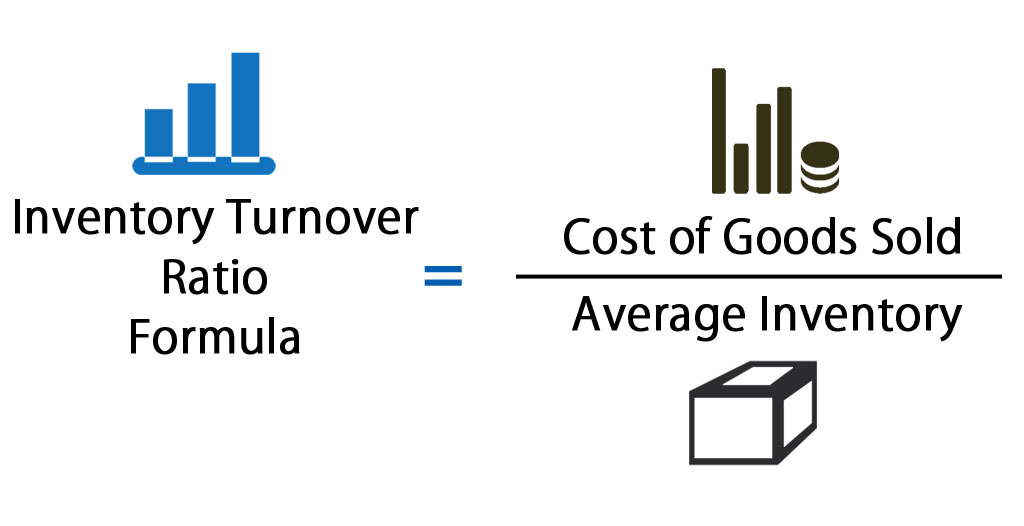
The accounts receivables turnover ratio is also known as the receivables turnover ratio, or just the turnover ratio for shortness. Net credit sales is the revenue generated when a firm sells its goods or services on credit on a given day – the product is sold, but the money will be paid later. To keep track of the cash flow (movement of money), this has to be recorded in the accounting books (bookkeeping is an integral part of healthy business activity). This legal claim that the customers will pay for the product, is called accounts receivables, and related factor describing its efficiency is called the receivables turnover ratio.
Step 2 of 3
In other words, Alpha Lumber converted its receivables (invoices for credit purchases) to cash 11.43 times during 2021. Since we already have our net credit sales ($400,000), we can skip straight to the second step—identifying the average accounts receivable. Most businesses operate on credit, which means they deliver the goods or services upfront, invoice the customer, and give them a set amount of time to pay.
Accounts Receivable (AR) Turnover Ratio Examples
Of course, it’s still wise to make sure you’re not too conservative with your credit policies, as too restrictive policies lead to loss of clients and slow business growth. Cleaning companies, on the other hand, typically require customer payment within two weeks. If you own one of these businesses, your idea of “high” or “low” ratios will be vastly different from that of the construction business owner. You can find the numbers you need to plug into the formula on your annual income statement or balance sheet.

Receivables Turnover Ratio: Formula, Importance, Examples, and Limitations
Accounts receivable turnover is an efficiency ratio or activity ratio that measures how many times a business can turn its accounts receivable into cash during a period. In other words, the accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how many times a business can collect its average accounts receivable during the year. As a reminder, this ratio helps you look at the effectiveness of your credit, as your net credit sales value does not include cash, since cash doesn’t create receivables.
You can learn more about GOBankingRates’ processes and standards in our editorial policy. By using this ratio, companies can evaluate their productivity in using assets that are on hand. By knowing how quickly your invoices are generally paid, you can plan more strategically because you will have a better handle on what your future cash flow will be. Though we’ve discussed how this metric can be helpful in assessing how long it takes your business to collect on credit, you’ll also want to remember that just like any metric, it has its limitations.
Limitations of Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
- The receivable turnover ratio, otherwise known as the debtor’s turnover ratio, is a measure of how quickly a company collects its outstanding accounts receivables.
- AR turnover is important because it can indicate the health of a company’s billing and collection processes.
- It is a quantification of a company’s effectiveness in collecting outstanding balances from clients and managing its line of credit process.
- The P-A-S method is more accurate than the traditional AR turnover calculation because it takes into account the timing of sales and collections.
- The accounts receivables turnover ratio is also known as the receivables turnover ratio, or just the turnover ratio for shortness.
- Accounts Receivable Turnover is a financial ratio that measures the efficiency with which a company collects payments from its customers.
Net credit sales are calculated as the total credit sales adjusted for any returns or allowances. Every company sells a product and/or service, invoices for the same, and collects payment according to the terms set forth in the sale. If a company is too conservative in extending credit, it may lose sales to competitors or incur a sharp drop in sales handr block, turbotax glitch may impact some stimulus checks from the irs when the economy slows. Businesses must evaluate whether a lower ratio is acceptable to offset tough times. The best way to not deal with Accounts Receivable problems is not to have accounts receivable. That might not be possible for all business but there many industries that are able to accept pre-payment before providing a good or service.
To find their accounts receivable turnover ratio, Centerfield divided its net credit sales ($250,000) by its average accounts receivable ($50,000). This ratio, together with average collection period ratio, indicates how quickly a business entity can be expected to convert its credit sales into cash and thus helps evaluate the liquidity of its receivables. Like some other activity ratios, receivables turnover ratio is expressed in times like 5 times per quarter or 12 times per year etc. Lastly, many business owners use only the first and last month of the year to determine their receivables turnover ratio.
Plus, addressing collections issues to improve cash flow can also help you reinvest in your business for additional growth. You should be able to find the necessary accounts receivable numbers on your balance sheet (as shown below). In this guide, therefore, we’ll break down the accounts receivable turnover ratio, discussing what it is, how to calculate it, and what it can mean for your business. If your accounts receivable turnover ratio is lower than you’d like, there are a few steps you can take to raise the score right away. If you have some efficient clients who are always on time with their payments, reward them by offering some discounts which will help attract more business without affecting your receivable turnover ratio.
